
PHP Rest API
In today’s interconnected digital world, building robust web applications often involves integrating data from various sources. PHP Rest API (Representational State Transfer Application Programming Interface) has emerged as a powerful solution for facilitating data communication between different systems. In this blog post, we’ll explore the world of PHP Rest API, its benefits, and how it simplifies the development of dynamic and data-driven web applications.
Table of Contents
What is PHP Rest API?
A PHP REST API is a web service that uses PHP programming language to implement a Representational State Transfer (REST) architecture. REST is a software design pattern that defines how web services should interact with each other over the internet. In a RESTful architecture, resources are identified by unique URLs, and actions are performed on these resources using standard HTTP methods (GET, POST, PUT, DELETE).
PHP is a popular programming language for building web applications, and it is often used to develop REST APIs. PHP REST APIs typically use JSON or XML format to transmit data, which can be easily consumed by other web applications, mobile applications, or devices.
With a PHP REST API, developers can create web services that expose data and functionality to other applications, allowing for interoperability and integration between different systems. RESTful APIs are widely used in web development because they are flexible, scalable, and can be easily adapted to different programming languages and platforms.
REST stands for “REpresentational State Transfer”. REST is an architectural style that defines a set of constraints for developing and consuming web services through the standard protocol (HTTP).
API stands for “Application Programming Interface”. It is a set of routines, protocols, and tools for creating software applications. An API interface makes communication possible between various software components.
REST API is the interface that allows mobile devices and web browsers (or also other web servers) to CRUD (create, read, update and delete) resources in the server respecting the REST rules (such as being stateless).
How Does REST API Work
REST requests are related to CRUD operations (Create, Read, Update, Delete) in the database, REST uses GET, POST, PUT and DELETE requests. Here below you can see what are the functions.
- GET – it is used to transfer data from client to server in HTTP protocol using URL String
- POST – it is also used to transfer data from client to server in HTTP protocol but it carries request parameters in the message body which makes it a more secure way
- PUT – This method request is used to enclosed the entity under the supplied Request URL.
- Options – It shows which technique is supportable.
- HEAD – It returns the meta-information.
Rest API Example
Let’s learn about REST API in PHP with the following example. Follow the below steps to create a simple REST API program in PHP using XAMPP on a local computer:
1). Create a database called “rest_api_php” from PHPMyAdmin
2). Once the database is created, run the following SQL command to create a table:
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS `order_transactions` ( `id` int(30) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `order_id` int(80) NOT NULL, `amount` decimal(10,2) NOT NULL, `response_code` int(10) NOT NULL, `response_desc` varchar(80) NOT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`id`), UNIQUE KEY `order_id` (`order_id`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=latin1 ;
Once the table is created with the above command, add some dummy data.
3). Now, create a file called “database.php” inside the “inc” directory of your project root directory for setup database connection. Add the following code to the “database.php” file:
$conn = mysqli_connect("localhost","root","","allphptricks");
if (mysqli_connect_errno()){
echo "Failed to connect to MySQL: " . mysqli_connect_error();
die();
}
4). Now create an “index.php” file in the root directory of your project and add the following code
<?php
header("Content-Type:application/json");
if (isset($_GET['order_id']) && $_GET['order_id']!="")
{
include('inc/database.php');
$order_id = $_GET['order_id'];
$result = mysqli_query(
$conn,
"SELECT * FROM `order_transactions` WHERE order_id=$order_id");
if(mysqli_num_rows($result)>0){
$row = mysqli_fetch_array($result);
$amount = $row['amount'];
$response_code = $row['response_code'];
$response_desc = $row['response_desc'];
response($order_id, $amount, $response_code,$response_desc);
mysqli_close($conn);
}
else
{
response(NULL, NULL, 200,"No Record Found");
}
}
else
{
response(NULL, NULL, 400,"Invalid Request");
}
function response($order_id,$amount,$response_code,$response_desc){
$response['order_id'] = $order_id;
$response['amount'] = $amount;
$response['response_code'] = $response_code;
$response['response_desc'] = $response_desc;
$json_response = json_encode($response);
echo $json_response;
}
5). Your application is completed. Now, you will get order transaction-related data by running the following URL where “rest-api” is the name of the project root directory.
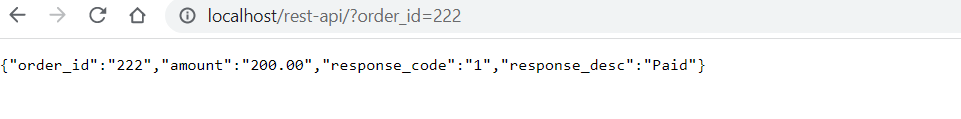
http://localhost/rest-api/?order_id=222
You will get output like following:
PHP Rest APIs have revolutionized the way web applications communicate and exchange data. By adhering to REST principles and leveraging the versatility of PHP, developers can create efficient and scalable APIs that power dynamic web applications. The benefits of PHP Rest APIs include simplified communication, scalability, reusability, and compatibility with a wide range of clients. Embrace the power of PHP Rest APIs to unlock endless possibilities for data integration, collaboration, and enhanced user experiences in your web applications.
I hope this article helps you to understand the basics of PHP REST API